Input sequence : format
Please input the nucleotide sequence only, or use the Fasta format.Examples:
- ATATGTGAT...
- atgatccgt...
- > Gene name...
ATGCCGTGAAATCGTCGATCG...
Description of the table
| Term | Description |
| Binding factor | The binding factor refers to the transcription factor regulating the gene. |
| Regulated gene | The first gene in the operon regulated by the transcription factor. |
| Promoter name | Some genes have more than two transcription start sites. To distiguish those promtoers, we show promoter names when they have. |
| Regulation | This column describes how the transcription factor regulates the gene. Options are positive, negative, both, promoter (in case of a sigma factor), and unknown. |
| Absolute position | We recalculated the absolute position of each cis-element using the NCBI sequence file (accession number AL645882). |
| Location | Location of the binding site with respect to the transcription start site. |
| Binding sequence (cis-element) | We show the cis-element as well as nearby sequences. Red characters correspond to the exact binding sequence, as shown in the reference. Bold face shows the transcription start site. |
| ND | No Data. |
Abbreviations of Experimental Techniques Used
| Abbrev. | Description |
|---|---|
| AR | DNA microarray and macroarray |
| CH | Chromatin immunoprecipitation microarray (ChIP-on-chip) |
| DB | Disruption of Binding Factor gene |
| DP | Deletion assay |
| FT | Footprinting assay (DNase I, DMS, etc.) |
| FP | Fluorecent protein |
| GS | Gel retardation assay |
| HB | Slot blot analysis |
| HM | Homology search |
| OV | Overexpression of Binding Factor gene |
| PE | Primer extension analysis |
| RG | Reporter gene (e.g., lacZ assay) |
| RO | Run-off transcription assay |
| ROMA | Run-off transcription followed by macroarray analysis |
| S1 | S1 mapping analysis (S1 nuclease transcript mapping) |
| RACE | 5'-RACE(Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) method |
| SDM | Site-directed mutagenesis (Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis) |
| ND | No Data |
Weight Matrix Search (by weight matrix)
This program returns the top 10 similar weight matrices against your input weight matrix.Use a tab (or space) deliminated format.
The first line, if starting with ">", is ignored.
Both absolute numbers and relative frequencies are acceptable.
Input nucleotides should be in the order A->C->G->T.
Example:
|
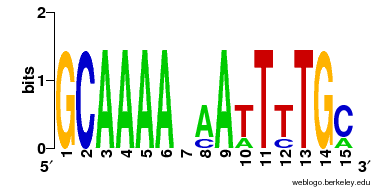
|
Example format 1:
>RocR
0 0 7 7 7 7 1 6 7 2 0 0 0 0 1
0 7 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 6
7 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 0 5 7 6 7 0 0
Example format 2:
0 0 1 1 1 1 0.143 0.857 1 0.286 0 0 0 0 0.143
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0.143 0 0 0 0.143 0 0 0.857
1 0 0 0 0 0 0.286 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0.571 0 0 0.714 1 0.857 1 0 0